Are you interested in getting a permanent life insurance plan because you want lifetime coverage for yourself? Well! You might find yourself confused between the options of whole life insurance vs indexed universal life.
Both of them are types of permanent insurance which share certain commonalities but also have significant differences between them. Understanding this difference would help you to meet your family’s needs efficiently and we will help you to better understand both of these policies.
In this blog post, we will discuss different aspects of whole life insurance vs indexed universal life so that you can make an informed decision for your family that fits your rights. Let’s get started!
What is Whole Life Insurance?
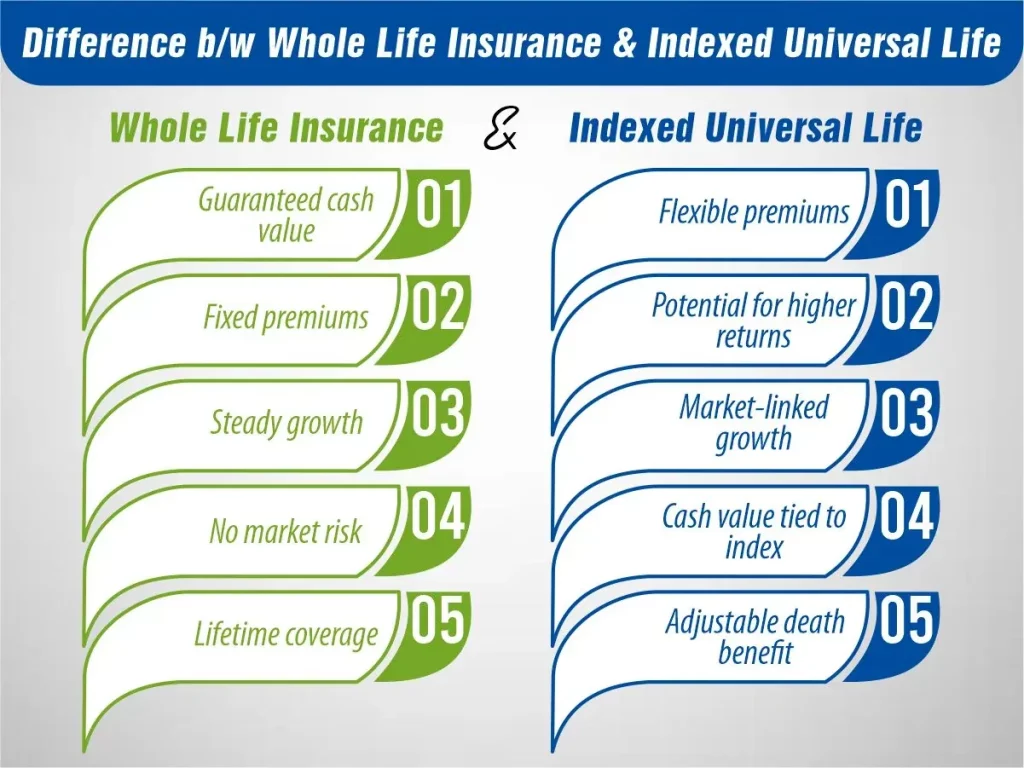
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers coverage to the policyholders for their entire life. Premiums usually remain constant throughout the policy ensuring stability and predictability in terms of costs. Moreover, whole life insurance also has a feature of cash value accumulation that can be accessed through policy loans or withdrawals within their lifetime.
Key Features of Whole Life Insurance:
- Guaranteed Death Benefit: Whole life insurance guarantees a death benefit payout to beneficiaries upon the insured’s passing, regardless of when it occurs, as long as premiums are paid.
- Cash Value Growth: A portion of the premiums paid into a whole life insurance policy accumulates as cash value, which grows on a tax-deferred basis over time.
- Fixed Premiums: Premiums for whole life insurance policies are typically fixed and do not increase over the life of the policy, providing budgetary stability for policyholders.
- Conservative Investment Strategy: Whole life insurance cash value grows at a guaranteed rate of return set by the insurance company, offering a conservative investment option.
Pros and Cons of Whole Life Insurance
Pros
- Assurance of Guaranteed Death Benefits
- Premiums Remain Fixed and Unaffected by Aging
- Flexibility in Payment Duration: Choose between 10 years, 20 years, or at age 65
- Ability to Utilize Cash Value Through Loans Later in Life
- Potential for Tax-Free Interest and Cash Disbursements
Cons
- Non-Guaranteed Interest Rates (Though Often with a Minimum Floor Rate)
- Potential for Missed Opportunities Due to Relatively Low-Interest Rates
- Lack of Premium Flexibility: Consistent Payments Required
What is Indexed Universal Life Insurance?
Indexed universal life insurance is also a type of permanent life insurance that provides coverage for the insured’s lifetime. However, unlike whole life insurance, indexed universal life offers flexibility in premium payments and potential cash value growth tied to the performance of a selected market index, such as the S&P 500.
-
Key Features of Indexed Universal Life Insurance:
- Flexible Premiums: Indexed universal life insurance policies allow policyholders to adjust their premium payments within certain limits, offering flexibility to accommodate changing financial circumstances.
- Potential for Cash Value Growth: Cash value accumulation in indexed universal life insurance is tied to the performance of a selected market index, offering the potential for higher returns compared to whole life insurance.
- Downside Protection: While indexed universal life insurance offers the potential for higher returns, most policies include a downside protection feature that prevents cash value from decreasing in the event of poor market performance.
- Tax-Deferred Growth: Similar to whole life insurance, cash value accumulation in indexed universal life insurance grows on a tax-deferred basis, allowing for potential tax advantages over time.
Pros and Cons of Indexed Universal Life Insurance
Pros
- Guaranteed benefits provide financial security.
- Flexibility in premium payments accommodates changing financial situations.
- Potential for higher interest earnings compared to traditional policies.
- Ability to borrow against policy’s cash value later in life.
Cons:
- Earnings tied to equity performance, subject to market volatility.
- Possibility of inferior returns if the index declines, though often with protective floors.
- Risk of premiums increasing over time.
- Complexity is introduced by complex derivative investments.
- Higher expenses compared to some other insurance options.
Comparing Whole Life Insurance vs Indexed Universal Life
When it comes to choosing between whole life insurance and indexed universal life (IUL) insurance, understanding the key differences is crucial. Let’s compare these two insurance options to help you make an informed decision:
1- Death Benefit Guarantee
Whole Life Insurance: Offers a guaranteed death benefit to beneficiaries, regardless of market conditions or policy performance.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Also provides a death benefit guarantee, but the cash value accumulation and potential payout are tied to the performance of a selected market index.
2- Premium Payments
Whole Life Insurance: Premiums are fixed and typically remain consistent throughout the life of the policy.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Premiums are more flexible, allowing policyholders to adjust payments within certain limits, and offering adaptability to changing financial circumstances.
3- Cash Value Growth
Whole Life Insurance: Accumulates cash value at a guaranteed rate of return set by the insurance company, providing stable but potentially lower returns compared to indexed universal life insurance.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Cash value growth is linked to the performance of a market index, offering the potential for higher returns but also subjecting the policy to market volatility.
4- Investment Strategy
Whole Life Insurance: Follows a conservative investment approach with guaranteed returns, focusing on stability and predictability.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Incorporates a more dynamic investment strategy, allowing for potential higher returns based on market performance, but also introducing greater investment risk.
5- Flexibility
Whole Life Insurance: Offers less flexibility in terms of premium payments and investment options, providing a straightforward and stable insurance solution.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Provides greater flexibility in premium payments and potential for cash value growth, catering to individuals seeking a more adaptable insurance and investment strategy.
6- Risk and Reward
Whole Life Insurance: Lower risk, lower potential reward, with guaranteed returns but limited growth.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Higher risk, higher potential reward, with the opportunity for greater growth but also subject to market fluctuations.
In a nutshell, whole life insurance prioritizes stability and predictability, making it suitable for individuals who prefer a conservative approach to insurance and investment. On the other hand, indexed universal life insurance offers flexibility and potential for higher returns, appealing to those comfortable with some level of investment risk and seeking greater growth opportunities.
Which Costs More: Whole Life Insurance vs Indexed Universal Life
Determining which costs more between whole life insurance and indexed universal life (IUL) insurance depends on various factors, including your age, health, coverage amount, and specific policy features. Let’s break down the cost considerations for each:
Whole Life Insurance Costs
- Premiums for whole life insurance policies are typically higher compared to term life insurance due to the permanent coverage and cash value accumulation feature.
- The premiums for whole life insurance are fixed and do not increase with age, providing stability and predictability in terms of cost.
- However, because of the guaranteed death benefit and cash value accumulation, whole-life insurance tends to have higher upfront costs compared to other types of insurance.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance Costs
- Premiums for indexed universal life insurance can vary depending on the policy’s design and the selected market index.
- Initially, premiums for indexed universal life insurance may be lower than whole life insurance, especially for younger policyholders, due to the flexibility in premium payments and the potential for higher returns based on market performance.
- However, indexed universal life insurance policies can become more expensive over time if the chosen market index underperforms or if the policyholder opts for additional riders or features, such as enhanced death benefits or accelerated benefit riders.
Choosing a Policy: Whole Life Insurance vs Indexed Universal Life
When deciding between whole life insurance and indexed universal life (IUL) insurance, it’s essential to consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and personal preferences. Let’s explore some key factors to help you make an informed decision:
Whole Life Insurance: If your primary goal is long-term financial security and stability, whole life insurance may be the right choice. It offers guaranteed death benefits and cash value accumulation, providing a reliable foundation for your financial plan.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: If you’re looking for flexibility and the potential for higher returns, indexed universal life insurance may better suit your needs. It allows you to participate in market growth while still offering a death benefit guarantee.
Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance follows a conservative investment approach with guaranteed returns, making it suitable for individuals with lower risk tolerance who prioritize stability.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Indexed universal life insurance introduces market risk, as the cash value growth is tied to the performance of a market index. It’s ideal for those comfortable with some level of investment risk and seeking greater growth potential.
Whole Life Insurance: Premiums for whole life insurance are fixed and typically remain consistent throughout the life of the policy, providing predictability and stability in terms of cost.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Premiums for indexed universal life insurance may vary depending on the policy’s design and market performance. It offers flexibility in premium payments, allowing you to adjust payments according to your financial situation.
Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance accumulates cash value at a guaranteed rate of return set by the insurance company, offering stable but potentially lower returns compared to indexed universal life insurance.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Indexed universal life insurance provides the potential for higher cash value growth based on the performance of a selected market index, offering the opportunity for greater returns over time.
Final Words
In conclusion, both whole life insurance vs indexed universal life insurance offer valuable benefits and features for individuals seeking permanent life insurance coverage. Your choice between the two will ultimately depend on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and personal preferences.
If you prioritize stability and predictability in premium payments and cash value growth, whole life insurance may be the right choice for you. On the other hand, if you’re comfortable with some level of investment risk and are seeking the potential for higher returns, indexed universal life insurance may better align with your objectives.